Over the years, the idea of an empire has changed considerably in the ever-changing world of global influence and power. Economic domination, military might, technological advancement, and cultural influence have evolved from what started as land conquests and extensive royal rule. By 2025, the conventional wisdom was that an empire encompassed not just the political domination of territories, but also the global influence of a country’s businesses, alliances, and soft power. Ancient Egyptians, Romans, and even the British Empire at its height all had their empires that influenced the development of their respective civilizations. A number of factors contributed to the growth of these empires, including control over resources, rule over varied populations, and influence over international trade routes. Empires nowadays are defined not just by the amount of land they control, but also by their influence on international politics, economic clout, and technological, military, and innovation prowess.
We are entering a time in 2025 when the power dynamics between states are becoming more intricate. A number of empires are reestablishing their power in ways that alter international dynamics, while others are resurging, changing, and creating new routes. The landscape of the world’s most powerful empires appears very different now than it did in the past due to new economic behemoths, changing political alignments, and technological breakthroughs in fields like space travel and artificial intelligence. Trade agreements, cyberwarfare, cultural exports, and geopolitical strategy are now all entangled with the idea of imperialism.
These Are The Top 10 List Of The Biggest Empires in World
1. The British Empire
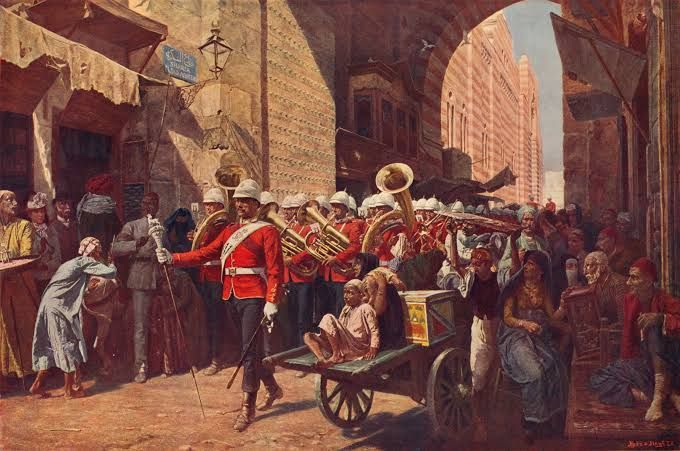

13.71 Million M2
The global and historical landscapes were transformed by the British Empire. Many parts of modern life, including language, culture, and international relations, continue to reflect its impact. Its formation occurred over many centuries as a result of trade, colonization, and war, with the nineteenth century seeing the bulk of its expansion. In terms of both population and territory, it was the greatest empire in history, spanning an estimated 13.71 million mi2 at its peak, which is over a fifth of the Earth’s total land area. There was a time when the expression “The sun never sets on the British Empire” was used to describe the vast network of colonies that made up the British Empire. The United Kingdom lost most of its colonial possessions after World War II, when imperialism in Britain started to decline. As one of the world’s most powerful nations, Britain is able to draw on the heritage of the British Empire to impact current events.
2. The Mongol Empire

9.27 million mi2
Spanning almost 9.27 million square kilometers throughout Eurasia, the Mongol Empire was massive by historical standards. Between 1206 until 1368, the empire was at the center of global history. When the Mongol tribes were united in the early thirteenth century by Genghis Khan, the Mongol Empire was born. Within fifty years, the empire had expanded its power over much of China and Central Asia in addition to a sizable portion of Eastern Europe. The boundaries of the Mongol Empire, which reached its zenith in the middle to late thirteenth century, extended from the Sea of Japan to western Anatolia, which is now Turkey. Despite this success, the events that led to the demise of the Mongolian Empire began with Genghis Khan’s death in 1227.
3. The Russian Empire
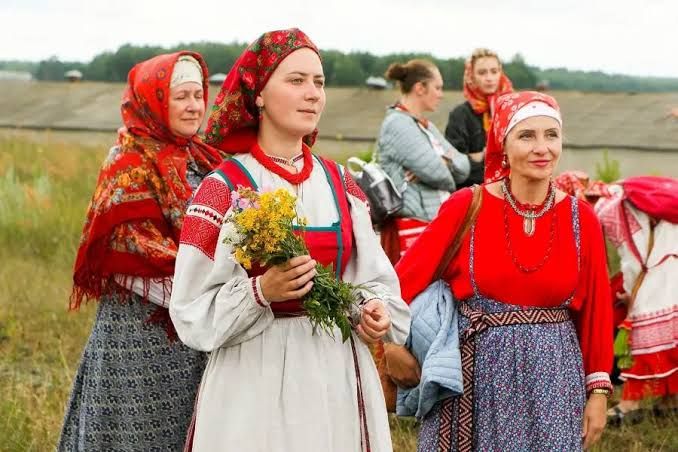

8.8 million mi2
From its foundation in 1721 until its dissolution in 1917, the Russian Empire was a massive political entity that dominated most of Eurasia. When it was at its largest in 1895, it covered 8.8 million square miles. During this time, the Russian Empire rose to prominence in Europe and was instrumental in stopping Napoleon’s conquests. A diverse group of 125.6 million people representing a wide range of ethnicities, faiths, languages, and geographical locations were subject to its rule. The Russian Senate bestowed the title of emperor upon Peter The Great (Peter I) on November 2, 1721, thus establishing the Russian Empire. An audacious mission to capture regions far and wide was shortly launched by the Emperor.
4. The Qing Dynasty

5.68 million mi2
The remarkable military campaigns of the Qing Dynasty are what made China famous and allowed the country to expand its borders. Between 1750 and 1790, during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor, 5.68 million mi2 of territory were added to China’s borders. This encompassed Taiwan, Tibet, Hainan, and a sizable portion of inner Asia that was either autonomous or ruled by another power at one point. The Qing were one of the most powerful imperial dynasties in history, extending their dominion over an estimated 450 million people through their sweeping campaigns. Agricultural output, commerce, and cultural life all saw increases during the relatively stable early Qing period, brought about by population growth. The demise would come as a result of this affluence, though.
5. The Spanish Empire

5.29 million mi2
Among the most formidable and enduring colonial empires in human history, the Spanish Empire stood tall and proud. It arose during the Age of Discovery in Europe, spearheaded by Spain and Portugal, and quickly rose to the status of world powerhouse. During its height in the late 1700s, the Spanish Empire, which lasted nearly five centuries (1492–1776), spanned about 5.29 million mi2. The Spanish colonial empire extended its influence across much of the Americas, the Caribbean, and beyond. In politics, culture, economics, and trade, the empire was a major player on a worldwide scale. Throughout most of what is now Latin America, North Africa, and Europe, the Spanish Empire was a powerful economic and military force during its heyday. Even now, its impact is palpable.
6. The Second French Colonial Empire
4.44 million mi2
At its height, the Second French Colonial Empire’s territories and dependents extended over 4.44 million mi2, making it one of the biggest empires in history. After the First French Colonial Empire collapsed, the Second French Empire rose to power in the early to mid-nineteenth century. France, like the United Kingdom, has numerous colonies around the globe in the past. Its African holdings were the most extensive, but its American, Caribbean, and South Pacific colonies were somewhat modest.
7. The Abbasid Caliphate

4.29 million mi2
The third Islamic Caliphate to follow the death of Islam’s founder, Prophet Mohammed, was the Abbasid Caliphate. After the Abbasids deposed the Umayyad Caliphate in the middle of the eighth century, the Caliphate was officially formed. Islamic history’s Golden Age started with the Abbasid Caliphate. The Caliphate’s eastern border with India and its westernmost extension to the coast of North Africa in what is now Algeria comprised a combined total of 4.29 million mi2. After decades of dwindling control beginning in the ninth century, the Abbasids were finally overthrown in the early sixteenth century.
8. The Umayyad Caliphate

4.29 million mi2
At its height, the Umayyad Caliphate extended over 4.29 million mi2, covering a large portion of what is now North Africa and the Middle East. Its reign lasted from 661 until 750. At 29% of the global population, it ranked among the greatest empires of all time. Although the Umayyad Caliphate did not exert direct control over the Sahara, the nomadic Berber tribes that lived there nonetheless paid respect to the caliph. Within the broader framework of the caliphate, local sultans and emirs exercised authority over their own territories. While the Umayyad Caliphate was in power, Islam spread throughout West Africa and Islamic culture flourished.
9. The Yuan Dynasty

4.25 million mi2
In the middle to late thirteenth century, when the enormous Mongol Empire split into several empires, the Yuan Dynasty arose to govern China. Kublai, whose real name was Emperor Shizu, was the fifth khagan emperor of the Mongol Empire and the man responsible for establishing the Yuan Dynasty. From 1271 until 1368, the vast expanse of land that is now China, Mongolia, and the Korean Peninsula were all under the power of the imperial rulers. This totaled 4.25 million mi2. The Ming Dynasty succeeded it in the 14th century, but its influence started to decline about the middle of that century.
10. The Xiongnu Empire

3.47 million mi2
At its height, the Xiongnu Empire was an ancient tribal confederation that covered 3.47 million square miles. The empire was established in the early third century BC by Modu Chanyu, a chief of the tribe. Nomadic peoples from the eastern Eurasian steppe, which the Mongols would subsequently conquer, made up the tribes that would eventually form the empire. Xiongnu Empire’s dominion, which peaked in the latter half of the 2nd century BC, embraced an area roughly centered on the Mongolian Plateau that extended from what is now China’s Manchurian region to the easternmost tip of Central Asia. In the first century AD, the Han Dynasty of China vanquished the Empire, causing the confederation to split in half.